Exposure to
harmful elements and toxic substances can affect human health.
Some substances can damage your skin and internal organs
(such as your heart, liver, kidneys and brain), cause asthma or other diseases,
including cancer.
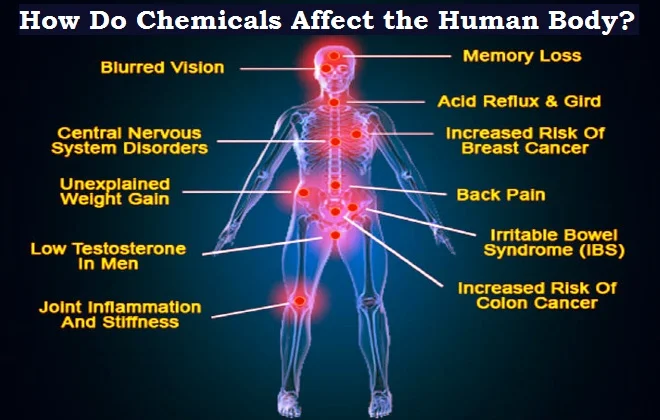 |
| Exposure to harmful substances can affect human health. |
How Do Harmful Elements and Chemicals Affect the Human Body?
Harmful Elements and
Hazardous Substances
On a daily
basis, a person is exposed to harmful substances that are dangerous to his
body, either in his workplace, in his home, or on the street.
Hazardous substances can be any substance, whether solid,
liquid, or gas, that may cause harm to human health.
It is important in the field of research on how these
substances and the harmful elements affect the body that distinguishes between
the terms of toxicity and hazard exposure.
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance can harm
an organism. It is the ability of a substance to produce undesirable effects in
the body.
Hazard exposure is a condition in which an individual or a
group of people remain at imminent risk of danger.
Consequently, the substance can be toxic, but it is not
dangerous if it is handled properly, it can be low toxic, but its degree of
severity is high.
How can Hazardous
Substances Enter the 'Body?
There are three main ways for substances to enter the body.
These are:
Ingestion: means eating something through the mouth, where a person can
eat food or drink contaminated with the toxic substance.
Absorption: As if the material comes into contact with the skin or eyes,
and this may cause a local effect, or it may be absorbed into the body.
Inhalation: where these substances enter the body through breathing and
this method is considered one of the most important ways of entering
substances, and toxic elements, into the body.
How Do Chemicals Affect the
Human Body?
The body's level of exposure to harmful substances and chemicals can be
classified as: acute (immediate) or chronic (long-term).
The chronic effect appears after exposure to harmful
substances for a long time.
The acute effect appears immediately after exposure to the
substance.
In a chronic effect, the body has been exposed to a dose of
the substance at specified stages during a specified period of time.
In an acute effect, the body has been exposed to a dose of
the substance in one batch so that the body has absorbed it quickly.
Harmful elements and toxic substances can damage your skin
and internal organs (such as your heart, liver, kidneys, and brain), cause
asthma or other diseases, including cancer.
What are the Effects of
Harmful Substances on the Body?
The way harmful substances affect the body can be classified
according to how they work:
Irritants: The substance to which the tissues were exposed caused a
state of instability in it, resulting in the emergence of a group of symptoms
on these tissues. Irritant substances may cause reversible inflammation or
irritation to a body surface, the eyes or airways after a single exposure.
Examples include paraben preservatives, ascorbic acid, and alpha-hydroxy acids
such as malic acid, glycolic acid, and lactic acid.
Asphyxiants: Asphyxiants displace oxygen in the ambient atmosphere and
thus cause a decrease in the amount of oxygen that reaches the tissues in those
who are exposed, leading to unconsciousness and death. Examples include carbon
dioxide, carbon monoxide, methane, and others.
Narcotics or Anesthetics: These substances affect the
functions of the central nervous system and cause this system to be inhibited.
A well-known example of these substances is chloroform.
Systemic Poisons: These poisons mainly destroy the body from the
inside, and affect its internal organs, such as those that affect the liver and
kidneys including inorganic lead and organophosphate insecticides.
Carcinogens: Exposure to these substances can increase the risk of
cancer. Examples include cadmium, radon, asbestos, nickel, benzene, benzidine,
and vinyl chloride.
Mutagens: These substances affect cells so that they mutate in them.
These may lead to cancer, or future changes to the cells of the body, including
radioactive materials.
Teratogens: If a pregnant woman is exposed to these substances, she may
give birth to a child with congenital anomalies such as thalidomide.
Sensitizers: These substances cause allergic symptoms in normal tissue
after repeated exposure to the chemical such as itching, shortness of breath,
and others, for example, dyes.
Tags
environmental exposures
harmful elements
health
health articles
health care
infectious diseases
